Difference Array Technique
This article will resolve
| LeetCode | Difficulty |
|---|---|
| 1094. Car Pooling | 🟠 |
| 1109. Corporate Flight Bookings | 🟠 |
| 370. Range Addition🔒 | 🟠 |
Prerequisite Knowledge
Before reading this article, you should first learn:
The Prefix Sum Technique is mainly used when the original array does not change, and you need to quickly find the sum of any interval. The key code is below:
class PrefixSum {
// prefix sum array
private int[] preSum;
// input an array to construct the prefix sum
public PrefixSum(int[] nums) {
// preSum[0] = 0, convenient for calculating cumulative sum
preSum = new int[nums.length + 1];
// calculate the cumulative sum of nums
for (int i = 1; i < preSum.length; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
}
// query the cumulative sum of the closed interval [left, right]
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
return preSum[right + 1] - preSum[left];
}
}class PrefixSum {
private:
vector<int> prefix;
public:
// prefix sum array
PrefixSum(vector<int>& nums) {
prefix = vector<int>(nums.size() + 1);
// calculate the cumulative sum of nums
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size() + 1; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
}
// query the cumulative sum of the closed interval [i, j]
int query(int i, int j) {
return prefix[j + 1] - prefix[i];
}
};class PrefixSum:
# Prefix sum array
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
self.prefix = [0] * (len(nums) + 1)
# Calculate the cumulative sum of nums
for i in range(1, len(self.prefix)):
self.prefix[i] = self.prefix[i - 1] + nums[i - 1]
# Query the cumulative sum of the closed interval [i, j]
def query(self, i: int, j: int) -> int:
return self.prefix[j + 1] - self.prefix[i]type PrefixSum struct {
// prefix sum array
prefix []int
}
// input an array, construct the prefix sum
func Constructor(nums []int) *PrefixSum {
prefix := make([]int, len(nums)+1)
// calculate the cumulative sum of nums
for i := 1; i < len(prefix); i++ {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1]
}
return &PrefixSum{prefix}
}
// query the cumulative sum of the closed interval [i, j]
func (ps *PrefixSum) Query(i, j int) int {
return ps.prefix[j+1] - ps.prefix[i]
}class PrefixSum {
constructor(nums) {
// prefix sum array
this.prefix = new Array(nums.length + 1);
// calculate the cumulative sum of nums
for (let i = 1; i < this.prefix.length; i++) {
this.prefix[i] = this.prefix[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
}
// query the cumulative sum of the closed interval [i, j]
query(i, j) {
return this.prefix[j + 1] - this.prefix[i];
}
}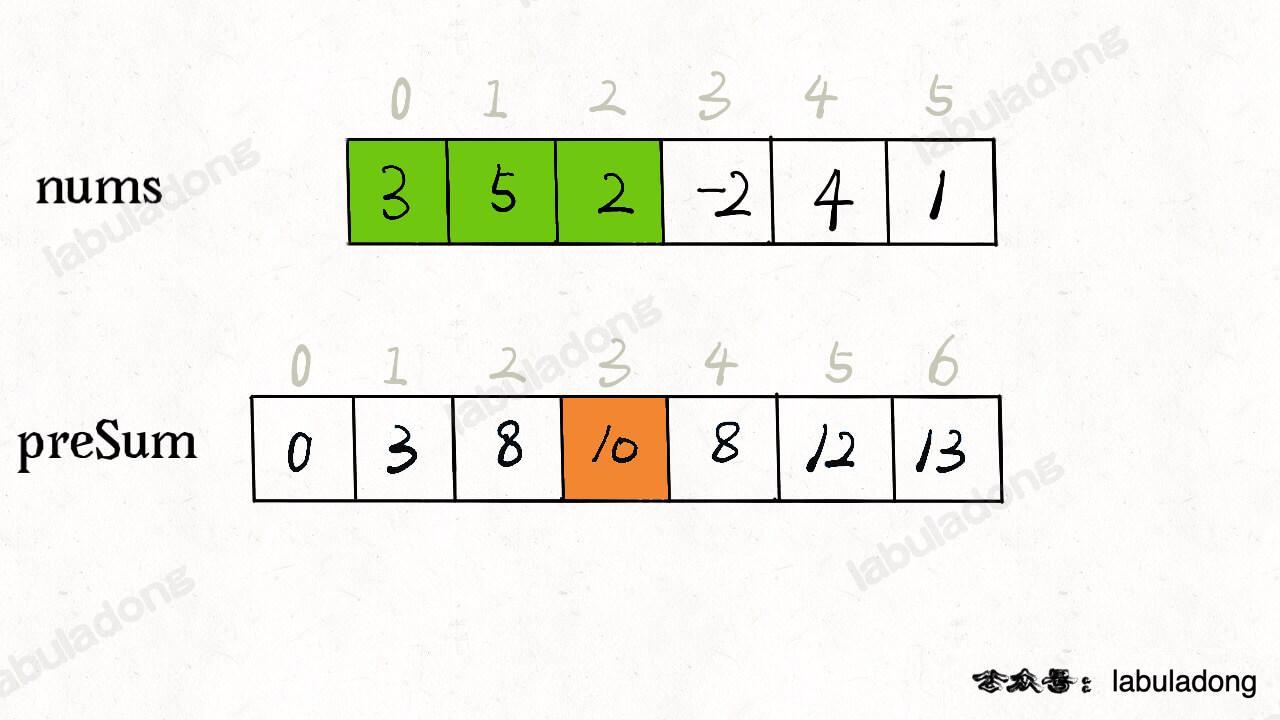
preSum[i] means the sum of all elements from nums[0] to nums[i-1]. If you want to find the sum from nums[i] to nums[j], just calculate preSum[j+1] - preSum[i]. You don't need to loop through the whole interval.
In this article, we talk about another technique similar to prefix sum: the Difference Array. The main use of the difference array is when you need to frequently increase or decrease the values in a range of the original array.
For example, suppose you have an array nums, and you need to:
- add 1 to all elements from
nums[2]tonums[6] - subtract 3 from all elements from
nums[3]tonums[9] - add 2 to all elements from
nums[0]tonums[4] - and so on...
After many such operations, what is the final value of the nums array?
The usual way is simple. If you want to add val to all elements from nums[i] to nums[j], just use a for loop and add val to each element. But this takes time for each operation. If there are many operations, this will be slow.
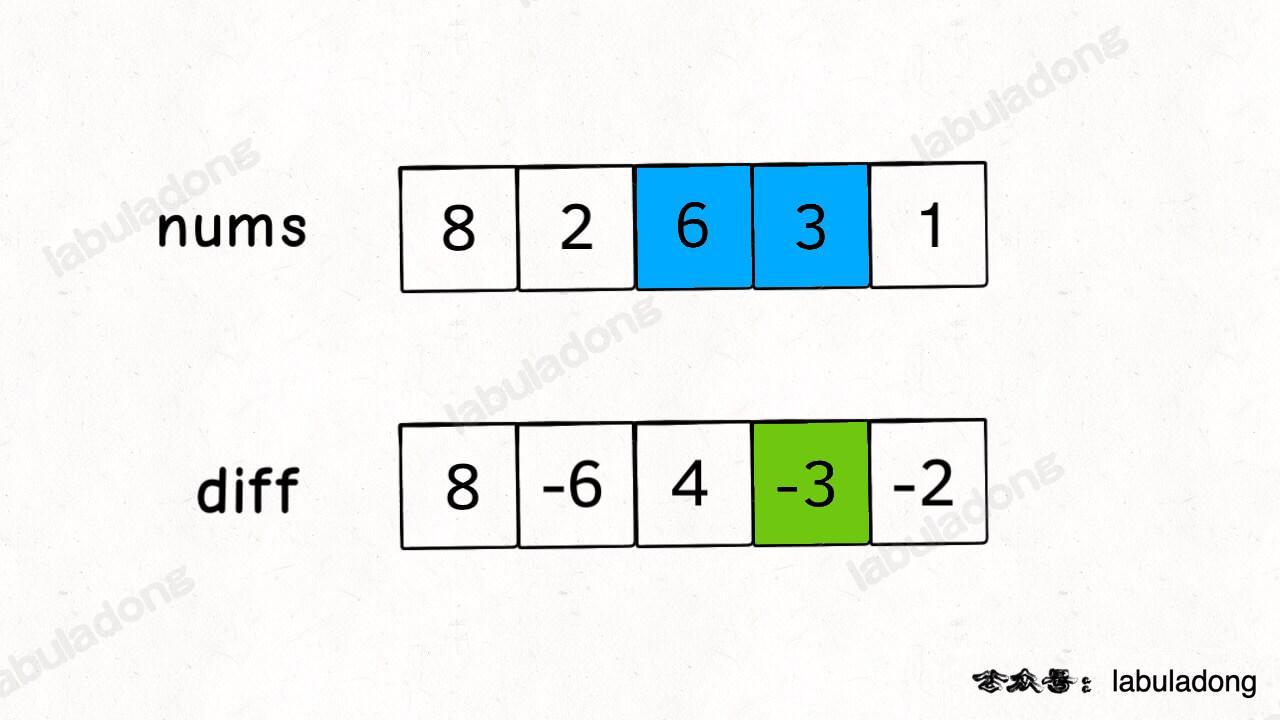
Here is where the difference array helps. Just like the prefix sum uses a preSum array, we can build a diff array for nums. diff[i] is the difference between nums[i] and nums[i-1]:
int[] diff = new int[nums.length];
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}int diff[nums.size()];
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}diff = [0] * len(nums)
# Construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1]// Construct the difference array
diff := make([]int, len(nums))
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i-1]
}var diff = new Array(nums.length);
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (var i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
Using this diff array, you can get back the original nums array. The code is like this:
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}int res[diff.size()];
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.size(); i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}res = [0] * len(diff)
# construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0]
for i in range(1, len(diff)):
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i]res := make([]int, len(diff))
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0]
for i := 1; i < len(diff); i++ {
res[i] = res[i-1] + diff[i]
}var res = new Array(diff.length);
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (var i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}With the difference array diff, you can quickly increase or decrease a range of elements. If you want to add 3 to all elements from nums[i] to nums[j], just do diff[i] += 3 and diff[j+1] -= 3:
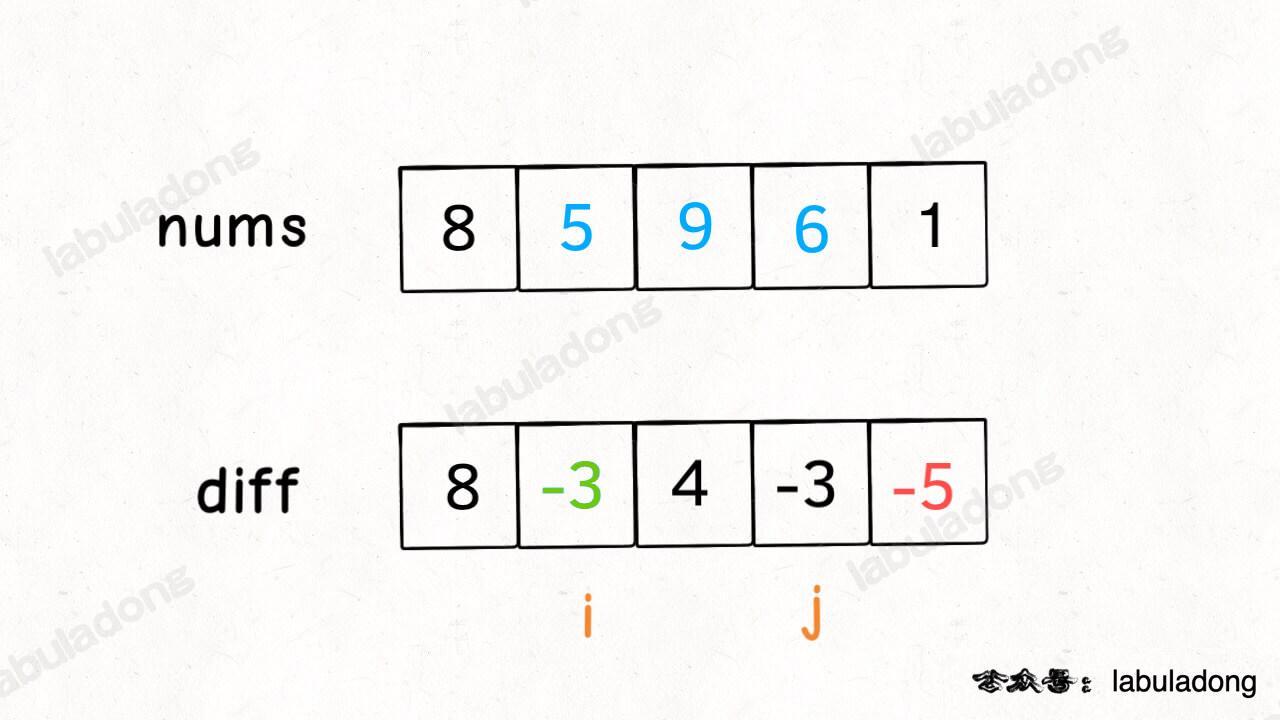
The idea is simple. When you set diff[i] += 3, it means you add 3 to all elements from nums[i] and after. Then diff[j+1] -= 3 means you subtract 3 from all elements from nums[j+1] and after. In total, only the elements from nums[i] to nums[j] get increased by 3.
You only need O(1) time to change the diff array, which is like updating an entire interval in the original nums array. Do all your changes to diff, then build the final nums from diff.
Now, let's make the difference array into a class with increment and result methods:
// Difference Array Utility Class
class Difference {
// difference array
private int[] diff;
// input an initial array, range operations will be performed on this array
public Difference(int[] nums) {
assert nums.length > 0;
diff = new int[nums.length];
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
public void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
public int[] result() {
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}// Difference Array Tool Class
class Difference {
// difference array
private:
vector<int> diff;
// input an initial array, range operations will be performed on this array
public:
Difference(vector<int>& nums) {
diff = vector<int>(nums.size());
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// add val (can be negative) to the closed interval [i, j]
void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.size()) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
vector<int> result() {
vector<int> res(diff.size());
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.size(); i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
};# Difference Array Tool Class
class Difference:
# difference array
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
assert len(nums) > 0
self.diff = [0] * len(nums)
# construct the difference array based on the initial array
self.diff[0] = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
self.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1]
# increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
def increment(self, i: int, j: int, val: int) -> None:
self.diff[i] += val
if j + 1 < len(self.diff):
self.diff[j + 1] -= val
# return the result array
def result(self) -> List[int]:
res = [0] * len(self.diff)
# construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = self.diff[0]
for i in range(1, len(self.diff)):
res[i] = res[i - 1] + self.diff[i]
return res// Difference array utility class
type Difference struct {
// difference array
diff []int
}
// Input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
func NewDifference(nums []int) *Difference {
diff := make([]int, len(nums))
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i-1]
}
return &Difference{diff: diff}
}
// Add val (can be negative) to the closed interval [i, j]
func (d *Difference) Increment(i, j, val int) {
d.diff[i] += val
if j+1 < len(d.diff) {
d.diff[j+1] -= val
}
}
// Return the result array
func (d *Difference) Result() []int {
res := make([]int, len(d.diff))
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = d.diff[0]
for i := 1; i < len(d.diff); i++ {
res[i] = res[i-1] + d.diff[i]
}
return res
}class Difference {
constructor(nums) {
// difference array
this.diff = new Array(nums.length);
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
this.diff[0] = nums[0];
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
this.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increase the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
increment(i, j, val) {
this.diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < this.diff.length) {
this.diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
result() {
let res = new Array(this.diff.length);
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = this.diff[0];
for (let i = 1; i < this.diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + this.diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}Notice the if statement in the increment method:
void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < sizeof(diff)/sizeof(int)) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}def increment(i: int, j: int, val: int) -> None:
diff[i] += val
if j + 1 < len(diff):
diff[j + 1] -= valfunc increment(i int, j int, val int) {
diff[i] += val
if j+1 < len(diff) {
diff[j+1] -= val
}
}var increment = function(i, j, val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
};When j+1 >= diff.length, it means you are changing all elements from nums[i] to the end, so you don't need to subtract val from diff anymore.
You can open the panel below. Click the line diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1] several times to see how the diff array is built. Then click df.increment a few times to see how the diff array changes:
Algorithm Visualization
Algorithm Practice
LeetCode Problem 370 "Range Addition" is a direct test of the difference array technique. You are given an array nums of length n, where all elements are 0. You need to increase or decrease the values of elements in given intervals, and finally return the updated nums array.
You can just copy the Difference class we wrote earlier to solve this problem:
class Solution {
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) {
// nums initialized to all 0s
int[] nums = new int[length];
// construct difference method
Difference df = new Difference(nums);
for (int[] update : updates) {
int i = update[0];
int j = update[1];
int val = update[2];
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
return df.result();
}
class Difference {
// difference array
private int[] diff;
public Difference(int[] nums) {
assert nums.length > 0;
diff = new int[nums.length];
// construct difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
public void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
public int[] result() {
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
// construct result array based on difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getModifiedArray(int length, vector<vector<int>>& updates) {
// nums initialized to all 0s
vector<int> nums(length, 0);
// construct difference method
Difference df(nums);
for (const auto& update : updates) {
int i = update[0];
int j = update[1];
int val = update[2];
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
return df.result();
}
class Difference {
// difference array
vector<int> diff;
public:
Difference(const vector<int>& nums) {
assert(!nums.empty());
diff.resize(nums.size());
// construct difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.size()) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
vector<int> result() {
vector<int> res(diff.size());
// construct result array based on difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < diff.size(); ++i) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
};
};class Solution:
def getModifiedArray(self, length: int, updates: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# nums initialized to all 0s
nums = [0] * length
# construct difference method
df = self.Difference(nums)
for update in updates:
i = update[0]
j = update[1]
val = update[2]
df.increment(i, j, val)
return df.result()
class Difference:
# difference array
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
assert len(nums) > 0
self.diff = [0] * len(nums)
# construct difference array
self.diff[0] = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
self.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1]
# increment closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
def increment(self, i: int, j: int, val: int):
self.diff[i] += val
if j + 1 < len(self.diff):
self.diff[j + 1] -= val
def result(self) -> List[int]:
res = [0] * len(self.diff)
# construct result array based on difference array
res[0] = self.diff[0]
for i in range(1, len(self.diff)):
res[i] = res[i - 1] + self.diff[i]
return resfunc getModifiedArray(length int, updates [][]int) []int {
// nums initialized to all 0s
nums := make([]int, length)
// construct difference method
df := NewDifference(nums)
for _, update := range updates {
i, j, val := update[0], update[1], update[2]
df.Increment(i, j, val)
}
return df.Result()
}
// Difference defines a difference array
// difference array
type Difference struct {
diff []int
}
// NewDifference creates a Difference instance
func NewDifference(nums []int) *Difference {
assert(len(nums) > 0)
diff := make([]int, len(nums))
// construct difference array
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i-1]
}
return &Difference{diff: diff}
}
// Increment increments a closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
// increment closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
func (d *Difference) Increment(i, j, val int) {
d.diff[i] += val
if j+1 < len(d.diff) {
d.diff[j+1] -= val
}
}
// Result constructs the result array based on the difference array
func (d *Difference) Result() []int {
res := make([]int, len(d.diff))
// construct result array based on difference array
res[0] = d.diff[0]
for i := 1; i < len(d.diff); i++ {
res[i] = res[i-1] + d.diff[i]
}
return res
}
// assert is a utility function to ensure a condition is met
func assert(condition bool) {
if !condition {
panic("condition failed")
}
}var getModifiedArray = function(length, updates) {
// nums initialized to all 0s
let nums = new Array(length).fill(0);
// construct difference method
let df = new Difference(nums);
// Correctly using the prototype methods of Difference
for (let update of updates) {
df.increment(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
return df.result();
};
// Define the Difference class
function Difference(nums) {
// difference array
this.diff = new Array(nums.length);
this.diff[0] = nums[0];
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
// construct difference array
this.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// Define increment method for Difference
Difference.prototype.increment = function(i, j, val) {
// increment closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
this.diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < this.diff.length) {
this.diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
};
// Define result method for Difference
Difference.prototype.result = function() {
let res = new Array(this.diff.length);
res[0] = this.diff[0];
for (let i = 1; i < this.diff.length; i++) {
// construct result array based on difference array
res[i] = res[i - 1] + this.diff[i];
}
return res;
};Of course, in real algorithm problems, you may need to think and abstract the problem. It won't always tell you directly to use the difference array. Let's look at LeetCode Problem 1109 "Corporate Flight Bookings":
1109. Corporate Flight Bookings | LeetCode | 🟠
There are n flights that are labeled from 1 to n.
You are given an array of flight bookings bookings, where bookings[i] = [firsti, lasti, seatsi] represents a booking for flights firsti through lasti (inclusive) with seatsi seats reserved for each flight in the range.
Return an array answer of length n, where answer[i] is the total number of seats reserved for flight i.
Example 1:
Input: bookings = [[1,2,10],[2,3,20],[2,5,25]], n = 5 Output: [10,55,45,25,25] Explanation: Flight labels: 1 2 3 4 5 Booking 1 reserved: 10 10 Booking 2 reserved: 20 20 Booking 3 reserved: 25 25 25 25 Total seats: 10 55 45 25 25 Hence, answer = [10,55,45,25,25]
Example 2:
Input: bookings = [[1,2,10],[2,2,15]], n = 2 Output: [10,25] Explanation: Flight labels: 1 2 Booking 1 reserved: 10 10 Booking 2 reserved: 15 Total seats: 10 25 Hence, answer = [10,25]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1041 <= bookings.length <= 2 * 104bookings[i].length == 31 <= firsti <= lasti <= n1 <= seatsi <= 104
The function signature is:
int[] corpFlightBookings(int[][] bookings, int n)vector<int> corpFlightBookings(vector<vector<int>>& bookings, int n)def corpFlightBookings(bookings: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[int]:func corpFlightBookings(bookings [][]int, n int) []intvar corpFlightBookings = function(bookings, n) {};This problem seems a bit tricky, but actually, it is still a difference array problem. Let me explain:
You are given an array nums of length n, where all elements are 0. You are also given a list bookings which contains several triplets (i, j, k). Each triplet means you need to add k to every element in the interval [i-1, j-1] in nums. Return the final nums array.
Note
Because the problem says n is counted from 1, but array indices start from 0, for each triplet (i, j, k), the interval in the array should be [i-1, j-1].
So, this is a standard difference array problem. We can reuse the class we wrote earlier:
class Solution {
public int[] corpFlightBookings(int[][] bookings, int n) {
// initialize nums as all 0
int[] nums = new int[n];
// construct the difference array
Difference df = new Difference(nums);
for (int[] booking : bookings) {
// note that converting to array index needs to subtract one
int i = booking[0] - 1;
int j = booking[1] - 1;
int val = booking[2];
// increment the range nums[i..j] by val
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
// return the final result array
return df.result();
}
class Difference {
// difference array
private int[] diff;
public Difference(int[] nums) {
assert nums.length > 0;
diff = new int[nums.length];
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
public void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
public int[] result() {
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> corpFlightBookings(vector<vector<int>>& bookings, int n) {
// initialize nums as all 0
vector<int> nums(n, 0);
// construct the difference array
Difference df(nums);
for (const auto& booking : bookings) {
// note that converting to array index needs to subtract one
int i = booking[0] - 1;
int j = booking[1] - 1;
int val = booking[2];
// increment the range nums[i..j] by val
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
// return the final result array
return df.result();
}
private:
class Difference {
// difference array
vector<int> diff;
public:
Difference(const vector<int>& nums) {
assert(!nums.empty());
diff.resize(nums.size());
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.size()) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
vector<int> result() {
vector<int> res(diff.size());
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < diff.size(); ++i) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
};
};class Solution:
def corpFlightBookings(self, bookings, n):
# initialize nums as all 0
nums = [0] * n
# construct the difference array
df = self.Difference(nums)
for booking in bookings:
# note that converting to array index needs to subtract one
i = booking[0] - 1
j = booking[1] - 1
val = booking[2]
# increment the range nums[i..j] by val
df.increment(i, j, val)
# return the final result array
return df.result()
class Difference:
# difference array
def __init__(self, nums):
assert len(nums) > 0
self.diff = [0] * len(nums)
# construct the difference array
self.diff[0] = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
self.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1]
# increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
def increment(self, i, j, val):
self.diff[i] += val
if j + 1 < len(self.diff):
self.diff[j + 1] -= val
def result(self):
res = [0] * len(self.diff)
# construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = self.diff[0]
for i in range(1, len(self.diff)):
res[i] = res[i - 1] + self.diff[i]
return resfunc corpFlightBookings(bookings [][]int, n int) []int {
// initialize nums as all 0
nums := make([]int, n)
// construct the difference array
df := NewDifference(nums)
for _, booking := range bookings {
// note that converting to array index needs to subtract one
i := booking[0] - 1
j := booking[1] - 1
val := booking[2]
// increment the range nums[i..j] by val
df.increment(i, j, val)
}
// return the final result array
return df.result()
}
type Difference struct {
// difference array
diff []int
}
func NewDifference(nums []int) *Difference {
if len(nums) == 0 {
panic("nums length must be greater than 0")
}
diff := make([]int, len(nums))
// construct the difference array
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i-1]
}
return &Difference{diff}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
func (d *Difference) increment(i, j, val int) {
d.diff[i] += val
if j+1 < len(d.diff) {
d.diff[j+1] -= val
}
}
func (d *Difference) result() []int {
res := make([]int, len(d.diff))
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = d.diff[0]
for i := 1; i < len(d.diff); i++ {
res[i] = res[i-1] + d.diff[i]
}
return res
}var corpFlightBookings = function(bookings, n) {
// initialize nums as all 0
let nums = new Array(n).fill(0);
// construct the difference array
let df = new Difference(nums);
for (let booking of bookings) {
// note that converting to array index needs to subtract one
let i = booking[0] - 1;
let j = booking[1] - 1;
let val = booking[2];
// increment the range nums[i..j] by val
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
// return the final result array
return df.result();
};
class Difference {
// difference array
constructor(nums) {
this.diff = new Array(nums.length).fill(0);
// construct the difference array
this.diff[0] = nums[0];
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
this.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
increment(i, j, val) {
this.diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < this.diff.length) {
this.diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// construct the result array based on the difference array
result() {
let res = new Array(this.diff.length);
res[0] = this.diff[0];
for (let i = 1; i < this.diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + this.diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}The problem is solved.
There is another similar problem: LeetCode Problem 1094 "Car Pooling":
1094. Car Pooling | LeetCode | 🟠
There is a car with capacity empty seats. The vehicle only drives east (i.e., it cannot turn around and drive west).
You are given the integer capacity and an array trips where trips[i] = [numPassengersi, fromi, toi] indicates that the ith trip has numPassengersi passengers and the locations to pick them up and drop them off are fromi and toi respectively. The locations are given as the number of kilometers due east from the car's initial location.
Return true if it is possible to pick up and drop off all passengers for all the given trips, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: trips = [[2,1,5],[3,3,7]], capacity = 4 Output: false
Example 2:
Input: trips = [[2,1,5],[3,3,7]], capacity = 5 Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= trips.length <= 1000trips[i].length == 31 <= numPassengersi <= 1000 <= fromi < toi <= 10001 <= capacity <= 105
The function signature is:
boolean carPooling(int[][] trips, int capacity);bool carPooling(vector<vector<int>>& trips, int capacity);def carPooling(trips: List[List[int]], capacity: int) -> bool:func carPooling(trips [][]int, capacity int) bool {}var carPooling = function(trips, capacity) {
};For example, with input:
trips = [[2,1,5],[3,3,7]], capacity = 4You cannot finish all trips in one go, because in trips[1], at most 2 more people can get in, otherwise the car will be overloaded.
You might have thought of using the difference array: Each trips[i] represents an interval operation; picking up and dropping off passengers is just like performing interval add and subtract operations on an array. If every element in the result array is less than capacity, then all trips can be completed without overloading.
But, what should be the length of the difference array (number of stations)? The problem does not give it directly, but does say:
0 <= trips[i][1] < trips[i][2] <= 1000Station numbers start from 0 up to 1000, so there are at most 1001 stations. We can set the length of the difference array to 1001. This way, all station indices are included:
class Solution {
public boolean carPooling(int[][] trips, int capacity) {
// at most there are 1000 stops
int[] nums = new int[1001];
// construct the difference array method
Difference df = new Difference(nums);
for (int[] trip : trips) {
// number of passengers
int val = trip[0];
// passengers get on at stop trip[1]
int i = trip[1];
// passengers get off at stop trip[2],
// meaning the interval passengers are on the car is [trip[1], trip[2] - 1]
int j = trip[2] - 1;
// perform interval operation
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
int[] res = df.result();
// the car should never exceed its capacity
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
if (capacity < res[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// difference array utility class
class Difference {
// difference array
private int[] diff;
// input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
public Difference(int[] nums) {
assert nums.length > 0;
diff = new int[nums.length];
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
public void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
public int[] result() {
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool carPooling(vector<vector<int>>& trips, int capacity) {
// at most there are 1000 stops
vector<int> nums(1001, 0);
// construct the difference array method
Difference df(nums);
for (const auto& trip : trips) {
// number of passengers
int val = trip[0];
// passengers get on at stop trip[1]
int i = trip[1];
// passengers get off at stop trip[2],
// meaning the interval passengers are on the car is [trip[1], trip[2] - 1]
int j = trip[2] - 1;
// perform interval operation
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
vector<int> res = df.result();
// the car should never exceed its capacity
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
if (capacity < res[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// difference array utility class
class Difference {
private:
// difference array
vector<int> diff;
public:
// input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
Difference(vector<int>& nums) {
assert(!nums.empty());
diff.resize(nums.size());
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
void increment(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.size()) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
vector<int> result() {
vector<int> res(diff.size());
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.size(); i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
};
};class Solution:
def carPooling(self, trips: List[List[int]], capacity: int) -> bool:
# at most there are 1000 stops
nums = [0] * 1001
# construct the difference array method
df = self.Difference(nums)
for trip in trips:
# number of passengers
val = trip[0]
# passengers get on at stop trip[1]
i = trip[1]
# passengers get off at stop trip[2],
# meaning the interval passengers are on the car is [trip[1], trip[2] - 1]
j = trip[2] - 1
# perform interval operation
df.increment(i, j, val)
res = df.result()
# the car should never exceed its capacity
for i in range(len(res)):
if capacity < res[i]:
return False
return True
# difference array utility class
class Difference:
# difference array
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
# input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
# construct the difference array based on the initial array
self.diff = [nums[0]] + [nums[i] - nums[i - 1] for i in range(1, len(nums))]
# increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
def increment(self, i: int, j: int, val: int) -> None:
self.diff[i] += val
if j + 1 < len(self.diff):
self.diff[j + 1] -= val
# return the result array
def result(self) -> List[int]:
res = [self.diff[0]]
# construct the result array based on the difference array
for i in range(1, len(self.diff)):
res.append(res[i - 1] + self.diff[i])
return resfunc carPooling(trips [][]int, capacity int) bool {
// at most there are 1000 stops
nums := make([]int, 1001)
// construct the difference array method
df := NewDifference(nums)
for _, trip := range trips {
// number of passengers
val := trip[0]
// passengers get on at stop trip[1]
i := trip[1]
// passengers get off at stop trip[2],
// meaning the interval passengers are on the car is [trip[1], trip[2] - 1]
j := trip[2] - 1
// perform interval operation
df.Increment(i, j, val)
}
res := df.Result()
// the car should never exceed its capacity
for _, v := range res {
if capacity < v {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// difference array utility class
type Difference struct {
}
// input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
func NewDifference(nums []int) *Difference {
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
diff := make([]int, len(nums))
diff[0] = nums[0]
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i-1]
}
return &Difference{diff: diff}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
func (d *Difference) Increment(i, j, val int) {
d.diff[i] += val
if j+1 < len(d.diff) {
d.diff[j+1] -= val
}
}
// return the result array
func (d *Difference) Result() []int {
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res := make([]int, len(d.diff))
res[0] = d.diff[0]
for i := 1; i < len(d.diff); i++ {
res[i] = res[i-1] + d.diff[i]
}
return res
}var carPooling = function(trips, capacity) {
// at most there are 1000 stops
const nums = new Array(1001).fill(0);
// construct the difference array method
const df = new Difference(nums);
for (const trip of trips) {
// number of passengers
const val = trip[0];
// passengers get on at stop trip[1]
const i = trip[1];
// passengers get off at stop trip[2],
// meaning the interval passengers are on the car is [trip[1], trip[2] - 1]
const j = trip[2] - 1;
// perform interval operation
df.increment(i, j, val);
}
const res = df.result();
// the car should never exceed its capacity
for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
if (capacity < res[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
// difference array utility class
class Difference {
// input an initial array, interval operations will be performed on this array
// construct the difference array based on the initial array
constructor(nums) {
// difference array
this.diff = [...nums];
this.diff[0] = nums[0];
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
this.diff[i] = nums[i] - nums[i - 1];
}
}
// increment the closed interval [i, j] by val (can be negative)
increment(i, j, val) {
this.diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < this.diff.length) {
this.diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
// return the result array
result() {
const res = new Array(this.diff.length);
// construct the result array based on the difference array
res[0] = this.diff[0];
for (let i = 1; i < this.diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i - 1] + this.diff[i];
}
return res;
}
}Now, this problem is also solved.
Difference array and prefix sum array are common and smart techniques. Each is suitable for different scenarios. If you understand them, they are easy to use.
Further Discussion
First question: To use the difference array, you need to create a difference array diff with the same length as the interval. What if the interval is huge, for example [0, 10^9]? Do you have to create an array of size 10^9 just to do interval operations?
Second question: Prefix sum can quickly do interval queries, and difference array can quickly do interval add/subtract. Can we combine them to quickly do both interval add/subtract and interval query at any time?
These two are common problems when dealing with interval questions. The best answer is a data structure called Segment Tree. It can do both interval add/subtract and interval query in time.